Dragon fruit is a lovely tropical fruit that is a native fruit of Central America, Southern Mexico, and along the Pacific coasts of Guatemala, Costa Rica, and El Salvador. The Botanical or scientific name of Dragon Fruit is Hylocereus Undatus and the local name of this fruit is Pitaya or Pitahaya.
After gaining worldwide popularity pitaya is now cultivated in almost all tropical and subtropical regions like East Asia, South Asia, Southeast Asia, the United States, the Caribbean, and Australia.
Contents

Why Pitaya is called Dragon Fruit?
There is an interesting story behind this. Pitaya’s scales resemble that of a dragon and the spikes resemble fire. So when the fruit was brought to Asia local people named it after the Chinese mythical creature dragon as “Dragon Fruit”. Now Pitaya is more popular as Dragon Fruit all over the world.
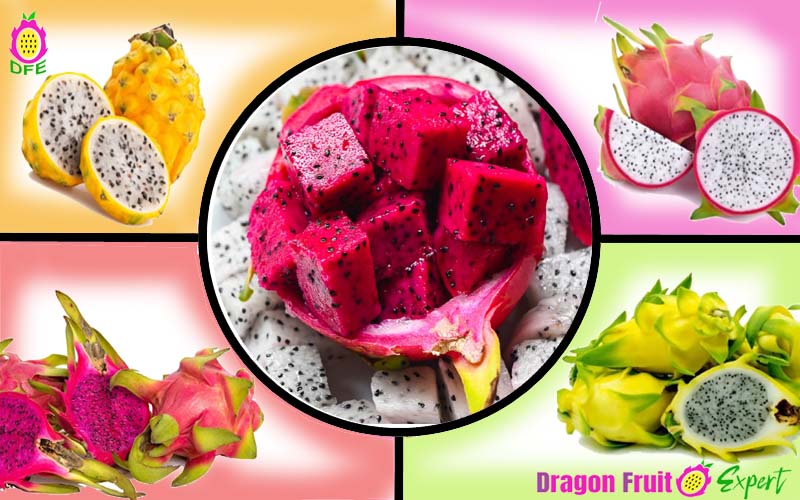
Different Varieties of Dragon Fruit.

There are several varieties of dragon fruits available according to their outer skin and inner flesh. The skin color may be pink, red, yellow, or orange, and the flesh color may be white, pink, red, or light violet with tiny black seeds. The most common variety is pink skin with white flesh. The taste of this fruit varies according to its inner color. More darker the inner more testier the fruit.
According to the taste the dragon fruits are divided into two categories, sweet and sour. The sweet category is more widely cultivated in comparison to the sour category.
Sour Dragon Fruit
This fruit variety is Stenocereus type. As the name suggests the taste of this variety is sour with edible seeds and a robust nutty flavour. This refreshing and spicy fruit is found throughout America. People in the northwestern Mexican region continue to harvest this fruit.
White Dragon Fruit
This is the most widely grown variety all over the world. The white Dragon Fruit is also termed as Hylocereus Undatus or Selenicereus Undatus. This sweet variety comes with pink skin and white flesh. The taste may vary according to the region and variety. For example, the Harpua has a semi-sweet pulp that tastes almost like a grape. Neitzel, a Californian native, is sweeter and more delicious when chilled.
Red Dragon Fruit
This variety of Dragon Fruit is termed as Pitaya Roja, Hylocereus costaricensis. This sweet variety comes with red flesh and red skin and its texture is comparable to a kiwi. Eating red dragon fruits can stain your hands. Red dragon fruit cultivars include Costa Rican Sunset (Natura Mystic), Zamorano, and Red Jaina.
Yellow Dragon Fruit
Termed as Pitaya megalanthus, scientifically Hylocereus Megalanthus, is also commonly known as Selenicereus Megalanthus. This dragon fruit variety comes with a yellow skin and firm white flesh and is native to South America. This fruit has only one variety and it is the tastiest.
Pink Dragon Fruit
This variety belongs to the red type, but the flesh is not the same. Pink dragon fruit comes with pink skin and soft to hot pink flesh. This fruit type is strong enough to adapt to different types of soil and climates. There are many pink dragon fruit varieties like Delight, Cosmic Charlie, Voodoo Child, and American Beauty (Hylocereus guatemalensis).

Nutritional Value of Dragon Fruit
| Nutritional value per 100 g (3.5 oz) | |
| Energy | 240 kJ (57 kcal) |
| Carbohydrates | 15.2 g |
| Sugars | 9.75 g |
| Dietary fiber | 3.1 g |
| Fat | 0.14 g |
| Protein | 0.36 g |
| Vitamins | Quantity |
| Folate (B9) | 7 μg |
| Choline | 5.1 mg |
| Vitamin C | 4.3 mg |
| Vitamin K | 4.4 μg |
| Minerals | Quantity |
| Calcium | 9 mg |
| Iron | 0.18 mg |
| Magnesium | 7 mg |
| Phosphorus | 12 mg |
| Potassium | 116 mg |
| Sodium | 1 mg |
| Other constituents | Quantity |
| Water | 84 g |
| Units μg = micrograms mg = milligrams IU = International units | |
Health Benefits of Dragon Fruit
Dragon fruit contains different types of useful antioxidants that protect human cells from unstable molecules called free radicals, which are linked to chronic diseases and aging.
Dragon fruit pulp contains antioxidants like Betalains, Hydroxycinnamates, and Flavonoids.
Betalains in Dragon Fruit
Dragon fruit, which comes in both red and yellow varieties, derives its vibrant color from two main types of betalains: betacyanins (red) and betaxanthins (yellow). The inclusion of betalains in dragon fruit may offer several potential health benefits:
- Antioxidant Properties: Helpful in neutralizing harmful free radicals in the body. Free radicals can cause cellular damage and are linked to various chronic diseases, such as cancer and cardiovascular conditions.
- Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Helpful in chronic inflammation is associated with several health issues, and consuming anti-inflammatory compounds like betalains may help alleviate inflammation.
- Cardiovascular Health: Helpful in cardiovascular well-being by reducing oxidative stress and inflammation. Additionally, research indicates potential positive effects on blood pressure levels.
- Liver Health: Limited studies suggest that betalains may have protective effects on the liver. While this could be beneficial for individuals with liver conditions, more research is required to substantiate these findings.
- Immune System Support: Antioxidants, including those found in betalains, play a role in supporting the immune system by shielding cells from oxidative stress. Consuming fruits like dragon fruit may provide additional support for immune function.
- Potential Anti-Cancer Properties: Preliminary research hints at the potential anti-cancer properties of betalains, particularly in inhibiting the growth of specific cancer cells. However, further investigation is necessary to fully comprehend these potential benefits.

Hydroxycinnamates in Dragon Fruit
The primary hydroxycinnamates in dragon fruit comprise chlorogenic acid, caffeic acid, and ferulic acid. These compounds offer potential health benefits:
- Antioxidant Properties: Hydroxycinnamates are recognized for their antioxidative activity, aiding in the neutralization of free radicals. Free radicals are unstable molecules that can cause cellular damage, contributing to aging and various diseases.
- Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Some research suggests that hydroxycinnamates, particularly chlorogenic acid, may possess anti-inflammatory properties. Chronic inflammation is associated with various health issues, including cardiovascular diseases and certain cancers.
- Cardioprotective Effects: The antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of hydroxycinnamates may contribute to cardiovascular health by protecting against oxidative stress and inflammation.
- Blood Sugar Regulation: Chlorogenic acid, a hydroxycinnamate found in dragon fruit, has been studied for its potential to regulate blood sugar levels. It may improve insulin sensitivity, reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes.
- Antimicrobial Activity: Some hydroxycinnamates, such as caffeic acid, exhibit antimicrobial properties. They may combat certain bacteria and fungi, providing support to the immune system.
- Neuroprotective Effects: Hydroxycinnamates, particularly ferulic acid, have been investigated for their potential neuroprotective effects. They may safeguard the brain from oxidative stress and inflammation, potentially lowering the risk of neurodegenerative diseases.
Flavonoids in Dragon Fruit
Flavonoids constitute a group of natural compounds known for their antioxidant properties, and they contribute significantly to promoting health. Below are the potential benefits associated with the flavonoids found in dragon fruit:
- Antioxidant Properties: The flavonoids in dragon fruit act as antioxidants, effectively neutralizing harmful free radicals within the body. This process is crucial in preventing oxidative stress, which is linked to various chronic diseases and the aging process.
- Anti-Inflammatory Benefits: Certain flavonoids present in dragon fruit display anti-inflammatory properties, helping to mitigate inflammation in the body. Chronic inflammation is associated with numerous health conditions, including heart disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer.
- Cardiovascular Support: Flavonoids have been linked to cardiovascular benefits, including the improvement of blood vessel function, reduction of blood pressure, and a lower risk of cardiovascular diseases. These effects contribute to overall heart health.
- Immune System Enhancement: Flavonoids may support the immune system by bolstering the body’s ability to combat infections.
- Potential Cancer Prevention: Some studies suggest that specific flavonoids may possess anti-cancer properties. While additional research is required, the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of flavonoids may contribute to cancer prevention.
- Neuroprotective Effects: Flavonoids may exhibit neuroprotective effects, promoting brain health and potentially reducing the risk of cognitive decline. These compounds help safeguard brain cells from damage and enhance cognitive function.
- Skin Health Support: Antioxidants, including flavonoids, play a vital role in maintaining healthy skin by protecting it from oxidative stress. This protective mechanism contributes to a more youthful appearance and helps prevent skin disorders.

Conclusion:
The presence of fat, protein, different types of vitamins, minerals, and strong antioxidants in dragon fruit makes it a super fruit. So add this fruit to your diet and make your immune system strong.









